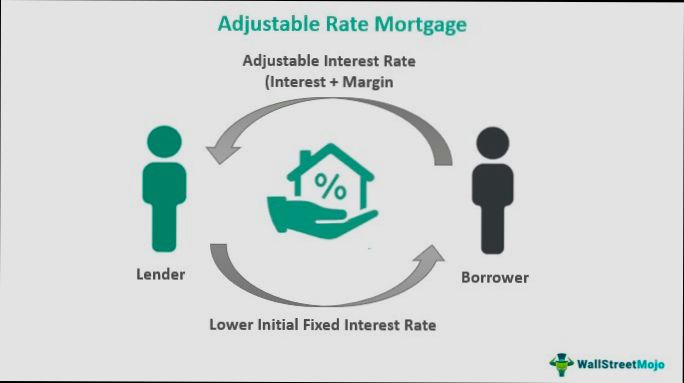
What is an Adjustable Rate Mortgage? In simple terms, it’s a home loan with an interest rate that changes over time, usually tied to a specific benchmark rate, like the LIBOR or the Treasury index. For instance, a popular option is the 5/1 ARM, where you enjoy a stable rate for the first five years, followed by annual adjustments thereafter. In today’s market, that initial rate can be significantly lower than fixed-rate mortgages—think about rates in the 3% range compared to fixed rates nudging toward 6% or higher.
Imagine you snag an ARM where your payments are more budget-friendly at the start; then, after five years, your rate might kick up. If rates go up by even a point, your monthly payment could jump by several hundred dollars. That’s a reality for many homeowners who opted for ARMs during the last boom, as they hoped to capitalize on that initial low rate. Knowing these details is vital if you’re considering your options, especially in a fluctuating market where interest rates can shift dramatically from year to year.

Understanding the Mechanics of ARMs
Adjustable Rate Mortgages (ARMs) are unique financial tools designed to provide homeowners with flexibility and potentially lower initial payments. It’s essential to dive deep into how they function, particularly the mechanics behind the interest rate adjustments, the loan structure, and how these factors can impact your overall financial viability.
One crucial aspect to understand about ARMs is the interest rate structure. Typically, ARMs start with a lower introductory interest rate for a specific period, which can range from one month to a decade. Here’s how that looks:
1. Initial Rate Periods: Many ARMs offer an initial rate that is significantly lower than traditional fixed-rate mortgages.
2. Adjustment Frequency: After the initial period, the interest rate may adjust annually or at another predetermined interval based on market rates.
3. Index and Margin: The new interest rate is calculated by adding a specific margin to an index rate (like the LIBOR or Treasury rates). This means if the index rises, your rate and payment will rise.
Key Components of Interest Rate Adjustments
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Index | A benchmark interest rate that reflects current market conditions (e.g., LIBOR, SOFR). |
| Margin | A fixed percentage added to the index that determines your mortgage interest rate. |
| Adjustment Cap | Limits how much the interest rate can increase at each adjustment period and over the life of the loan. |
| Lifetime Cap | A maximum limit on interest rate increases throughout the duration of the mortgage. |
Understanding these components helps clarify how changes in the index will affect your payments. For instance, if your initial rate is 3% for the first five years, and then the index rises significantly, your new rate could be calculated using the index value plus the margin. If the index shifts from 2% to 5%, that raises your new interest rate to 8%, depending on the margin.
Real-World Examples of ARMs in Action
1. Example of Initial vs. Adjusted Rates: Imagine you take out a 5/1 ARM with an initial rate of 3% for the first five years. After that period, if the index rises and the calculation results in a new rate of 4.5%, your monthly payments will increase from, say, $1,420 to $1,570, impacting your budget significantly.
2. Adjustment Caps: Let’s say an ARM has a 2% adjustment cap annually and a lifetime cap of 5%. If you start at an interest rate of 3%, the highest rate you would encounter at any point in the life of the loan would be 8%. It’s important to read your loan’s terms to understand these limits clearly.
Practical Implications for Homeowners Considering ARMs
- Budgeting for Increased Payments: Always plan ahead for the possibility of increased payments. It’s crucial to calculate what your maximum payment will be should rates rise to their caps.
- Comparing Loan Options: Compare ARMs to fixed-rate mortgages not only in terms of the initial interest rate but also potential future payments based on index trends.
- Market Awareness: Stay informed about economic changes that can affect interest rates. For example, if inflation is rising, that can lead to higher increase in indices, affecting your ARM payments sooner than expected.
Specific Facts About ARMs
- Currently, around 30% of new mortgages are ARMs, a significant rise from previous years.
- The average initial fixed-rate period for ARMs is about 5 years, after which adjustments occur based on pre-set intervals.
- Homeowners should be prepared for potential payment increases of up to 5% over the life of the loan, as indicated by standard adjustment caps.
By understanding the intricacies of how ARMs operate, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals and manage the potential risks and rewards associated with these types of loans.

Comparative Analysis of Fixed vs. Adjustable Rates
When contemplating a mortgage, one of the most critical decisions you’ll face is whether to choose a fixed-rate or an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM). Each option presents unique advantages and challenges, impacting your financial commitments in different ways.
Key Differences in Rate Structure
- Fixed Rates: With a fixed-rate mortgage, your interest rate remains constant throughout the life of the loan. This stability can be particularly comforting when market conditions fluctuate.
- Adjustable Rates: Conversely, ARMs typically begin with a lower initial rate that adjusts after a predetermined period. These rates can vary significantly based on market conditions, which can lead to lower monthly payments at the outset.
Rate Statistics to Consider
- According to recent data, fixed-rate mortgages generally offer rates approximately 1% to 2% higher than the initial rate of an ARM.
- Over the first five years, borrowers with ARMs may save an average of $200 to $300 per month compared to those with fixed rates, emphasizing the immediate financial benefits of ARMs.
Comparative Rate Table
| Feature | Fixed Rate | Adjustable Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate Stability | Constant throughout the loan term | Fluctuates based on market rates |
| Initial Rates | Higher than ARMs | Generally lower |
| Monthly Payment | Predictable & unchanging | Variable & potentially lower |
| Long-term Cost | Generally higher overall cost | Potentially lower, but uncertain |
| Risk of Rate Increases | None | Yes, after initial period |
Real-World Examples
Consider Jane and John, who are both purchasing homes priced at $250,000. Jane opts for a fixed-rate mortgage at 5%, while John chooses an ARM with an initial rate of 3%.
- Monthly Payments:
- Jane’s fixed payment is approximately $1,500.
- John’s initial payment is about $1,050, saving him $450 monthly in the short term.
After five years, if John’s rate adjusts to 4%, his new payment of $1,250 still reflects a long-term cost advantage compared to Jane’s fixed rate. However, as rates may continue to rise, John’s payment could surpass Jane’s if market conditions shift significantly.
Practical Implications for You
- Discounted Initial Payments: If you’re planning to move or refinance within a few years, an ARM can be financially advantageous due to the lower initial payments.
- Long-term Perspective: If you plan to stay in your home long-term, a fixed-rate may provide peace of mind and predictability in your budgeting.
Actionable Insights
- Evaluate Your Financial Situation: Assess how sensitive you are to fluctuations and whether you can handle increased payments in the future.
- Explore Market Conditions: Stay informed about interest rate trends. If rates are projected to rise, securing a fixed mortgage might be the wiser choice.
- Consider Your Homeownership Plans: If you anticipate moving before the rate adjustments kick in, leaning toward an ARM could yield immediate savings.
By understanding these nuanced differences between fixed and adjustable rates, you can make a more informed decision that aligns with your financial goals.
Benefits of Choosing an Adjustable Rate Mortgage
Adjustable Rate Mortgages (ARMs) come with unique benefits that can be quite appealing for prospective homeowners. Understanding these advantages helps you make an informed decision about your mortgage choice. Let’s explore the key benefits that ARMs offer, backed by research data.
Lower Initial Payments
One of the most significant benefits of an ARM is the potential for lower initial monthly payments compared to fixed-rate mortgages. Research shows that the first five years of an ARM can offer interest rates that are typically 1% to 2% lower than fixed rates. This means more cash flow for you at the beginning of your homeownership journey.
Rate Caps for Added Protection
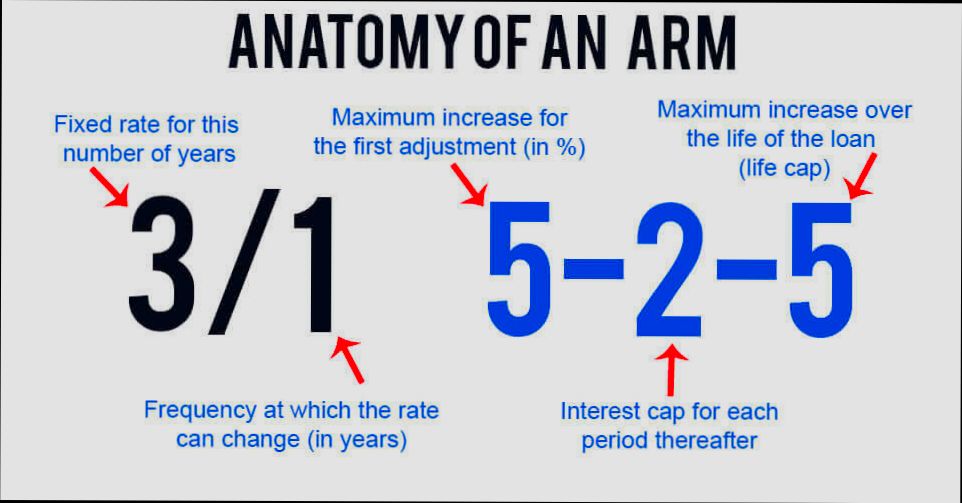
ARMs often include rate caps that limit how much your interest rate can increase during adjustments. For example:
| Adjustment Period | Initial Rate | Maximum Increase |
|---|---|---|
| 5/1 ARM | 3% | 2% |
| 7/1 ARM | 3.5% | 2.5% |
| 10/1 ARM | 4% | 3% |
These caps can protect you from steep increases, making it easier to budget for future payments. You can enjoy peace of mind knowing your rates won’t spike unexpectedly.
Flexible Loan Terms
ARMs offer flexibility in loan terms that can greatly benefit your financial situation. The shorter the fixed-rate period, the more you can save initially. For example, choosing a 7/1 ARM allows five straightforward years of lower payments, which can translate into significant savings. These savings can be utilized for renovations, savings, or other investments.
Potential for Savings with Market Drops
If market interest rates decrease, there’s a possibility that your ARM’s rate will adjust downward. This opportunity falls heavily in your favor, as you could benefit from lower payments without refinancing. For instance, if a typical home buyer with a fixed-rate mortgage finds themselves locked into a higher rate, those with ARMs can see potential reductions in their monthly obligations.
Real-World Examples
Consider Sarah, who took out a 5/1 ARM at a 2.8% initial interest rate. Over the first five years, she saved approximately $200 monthly compared to the fixed-rate option. With those savings, she built an emergency fund and invested in home improvements. After five years, when her rate adjusted, she comfortably budgeted for the increase due to her savings plan.
In another example, John opted for a 10/1 ARM. As interest rates fell during his term, he found his maximum interest increase was capped at 3%. When his rate adjusted, he only saw a modest increase, which he had anticipated and planned for, proving the flexibility an ARM can provide.
Practical Implications
When considering an ARM, take note of your long-term plans. If you expect to move or refinance within a few years, an ARM can be particularly advantageous. Keeping abreast of market trends can also inform your decision, as ARMs might allow you to capitalize on favorable rates.
Actionable Advice
Before committing to an ARM, carefully analyze your financial situation. Here are some steps to consider:
- Calculate potential savings over the initial years versus a fixed-rate mortgage.
- Assess how long you plan to stay in the home and if those plans align with the ARM’s structure.
- Consider consulting with a mortgage advisor who can help you navigate the specifics of various ARM options.
By understanding these benefits, you can make a sound decision that aligns with your financial goals.

Real-World Scenarios for ARMs
Adjustable Rate Mortgages (ARMs) can be beneficial in various real-world contexts, depending on individual financial situations and market conditions. Understanding how ARMs play out in specific scenarios allows you to make informed decisions tailored to your circumstances.
Scenarios to Consider
1. Short-Term Homeownership:
- If you’re planning to stay in a home for a short period (e.g., 3-5 years), an ARM often presents lower initial payments. For instance, many ARMs offer introductory rates that are significantly lower than fixed rates, potentially saving you thousands initially.
2. Market Fluctuations:
- In times of economic uncertainty, interest rates may fluctuate. ARMs can appeal to those who anticipate benefiting from lower rates in the long term. For example, if you secure an ARM with a 2% initial rate before a rate increase, your savings can be substantial compared to fixed options.
3. Income Growth Expectation:
- If you expect your income to rise significantly over the upcoming years, locking in a lower initial rate with an ARM may help manage monthly payments until you reach a higher salary. If future income increases by an estimated 20% over five years, you’ll be better positioned to adjust to potential rate hikes.
| Scenario Type | Benefits of ARMs | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Short-Term Homeownership | Lower initial payments | Risk of rate increases post-adjustments |
| Market Fluctuations | Potential for favorable rate adjustments | Market conditions can be unpredictable |
| Income Growth Expectation | Alleviates short-term financial strain | Anticipated income must be reliable |
Real-Life Example: The Smith Family
Consider the Smith family, who purchased their first home in 2022. They opted for a 5/1 ARM, which offered an initial rate of 2.5%. Over the first five years, their monthly payment remained stable, allowing them to invest in other areas like home renovations and savings. By the time their rate adjusted, they were ready for the change, as they had secured promotions at work with a corresponding 30% increase in household income.
Practical Insights
- Monitor Market Trends: Staying informed about interest rate trends can help you determine the best time to switch to a fixed mortgage or refinance your ARM.
- Assess Financial Health: Ensure that your financial situation can comfortably absorb potential payment increases. Use financial calculators to project future payments based on various rate scenarios.
- Consider Cap Structures: Look for ARMs with rate caps. For instance, a cap that restricts the rate increase to a maximum of 2% per adjustment can protect you from extreme fluctuations.
Actionable Tips
- If you choose an ARM, regularly assess your financial situation and local market conditions to prepare for adjustments.
- Consulting with a financial advisor can provide personalized insights based on your plans, helping you decide which ARM products align with your financial goals.
- Consider making extra payments during the initial fixed period to pay down principal, which can reduce the impact of future rate adjustments.

Recent Trends and Statistics on ARMs
The adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) landscape is shifting in response to market dynamics and consumer preferences. As more borrowers seek flexible financing options, understanding recent trends and statistics related to ARMs can equip you with valuable insights for making informed decisions.
Current Popularity and Market Share
Recently, ARMs have gained significant traction among homeowners. As of early 2023, approximately 15% of all new mortgage applications were for ARMs, a notable increase from just 1% in late 2020. This upward trend highlights a growing acceptance of variable-rate products amid fluctuating interest rates.
Interest Rate Movements
- The average initial interest rate for 5/1 ARMs has hovered around 3.25%, while the average rate for 30-year fixed mortgages remains closer to 5.5%.
- Approximately 70% of borrowers opting for ARMs did so thinking their rates would remain manageable compared to fixed-rate alternatives, reflecting a shift in consumer confidence.
| Year | % of Mortgage Applications for ARMs | Average Initial Rate (5/1 ARM) | Average 30-Year Fixed Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1% | 2.75% | 3.25% |
| 2021 | 5% | 3.00% | 3.50% |
| 2022 | 10% | 3.10% | 4.25% |
| 2023 | 15% | 3.25% | 5.50% |
Key Demographic Shifts
You might find it interesting that younger homeowners are increasingly opting for ARMs. In fact, nearly 40% of first-time homebuyers under 30 years old are choosing ARMs, largely driven by affordability concerns. This demographic is particularly drawn to the potential for lower monthly payments during the introductory period.
Real-World Case Studies
Consider Maria and Tom, a young couple who purchased their first home in May 2023 using a 5/1 ARM. With an initial rate of 3.3%, their monthly payment was significantly lower than what they might have paid with a fixed-rate mortgage at around 5.5%. They plan to sell or refinance within five years, allowing them to take advantage of the lower starting rates without facing the potential consequences of rate increases.
Another case involved a growing family that secured a 7/1 ARM in January 2023, allowing them to have lower payments while deciding if they would need to upsize in five years. The family embraced the fluctuation of early rates, which were appealing to them amidst increasing home prices.
Practical Implications
Given the emerging trends, it’s essential to assess how ARMs align with your financial goals.
- If you’re considering an ARM, analyze the potential rate adjustments and how they could fit into your long-term plans.
- Keep an eye on economic indicators, as rising inflation may impact future adjustment rates, leading you to make proactive financial decisions.
Lastly, think about the period of holding your mortgage: if your future plans involve moving or refinancing within the ARM’s initial term, you might benefit the most from these products.
By keeping abreast of ARMs’ evolving landscape, you can position yourself effectively in a changing home financing environment.

Potential Risks Associated with Adjustable Rates
When considering an Adjustable Rate Mortgage (ARM), it’s essential to understand not just the benefits but also the potential risks that come with it. As these loans are subject to interest rate changes, several factors can lead to unexpected financial strain. Let’s dive into these risks and explore what they mean for you.
Interest Rate Volatility
One of the most significant risks tied to ARMs is interest rate volatility. Since rates can fluctuate based on market conditions, you might find your monthly payment increasing dramatically once the fixed-rate period ends.
- Impact of Rate Increases: For instance, if rates increase by just 2% after the initial period, your monthly payment could increase significantly, potentially affecting your budget.
Payment Shock
Payment shock occurs when your monthly payments rise sharply after the initial low-rate period, which can be financially overwhelming.
- Example of Payment Shock: Suppose an ARM starts with a low rate of 3% for the first five years. If it adjusts to a higher rate of 5% or 6%, this translates to a substantial increase in your monthly payments, leaving you potentially unprepared for the added costs.
Rate Caps May Not Sufficiently Protect You
While ARMs often include rate caps to limit how much your interest can rise at each adjustment, these caps may not fully mitigate the increases you face.
- Understanding Cap Structures: A typical cap might allow a maximum increase of 2% per adjustment period. If interest rates soar in the market, you could still end up with a rate that, while capped, is significantly higher than your initial interest, creating a disconnect from your financial planning.
| Adjustment Period | Initial Rate | Possible Increase | Maximum Rate with Cap |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Year | 3% | 2% | 5% |
| 3 Year | 2.5% | 2% | 4.5% |
| 5 Year | 4% | 2% | 6% |
Limited Predictability
Predicting future market trends can be tricky, and the unpredictability of how rates will adjust can add a layer of stress to your financial planning.
- Risk Example: If you anticipate that your rate won’t exceed a certain percentage based on historical trends, and then the market takes an unexpected turn, you may find yourself unprepared for a significant hike that strains your finances.
Potential for Negative Amortization
In some cases, if your ARM has options like low initial payments, you could experience negative amortization, where your loan balance increases instead of decreases.
- Negative Amortization Explanation: Say your monthly payments aren’t covering the interest accrued; thus, the remaining balance grows. This situation can arise unexpectedly, especially if rates spike, leaving borrowers with a heavier debt load than anticipated.
Practical Takeaways
Understanding these risks can help you make informed decisions. Here are some actionable insights:
- Evaluate Your Budget: Prepare for potential payment increases by evaluating your financial cushion. This could mean setting aside extra savings to offset potential future rate hikes.
- Consider Lock-in Options: Some lenders offer the ability to lock in rates for a longer term. While this might come with a cost, it can provide peace of mind regarding your future payments.
- Engage Financial Counsel: Consulting with a financial advisor can help you create a tailored plan, especially in assessing whether an ARM aligns with your long-term financial goals.
Finally, be aware that staying informed about market trends and understanding the specific terms of your ARM will play a crucial role in managing these potential risks effectively. The more proactive you are in planning for these situations, the better your financial stability will be!

Impact of Market Changes on ARM Payments
The fluctuating nature of interest rates significantly affects adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) payments. Understanding how market conditions impact these payments is crucial for managing your budget effectively and ensuring long-term financial health. In this section, we’ll dive into how market changes shape ARM payments, emphasizing the tangible data and practical steps you can take.
Key Points on Market Impact
- First Adjustment Signal: After the initial fixed-rate period, market conditions will determine your first adjustment. If interest rates rise, you may see a notable increase in your monthly payments.
- Cap Limitations: Most ARMs come with caps that limit how much your interest rate can increase during the first adjustment. For example, with a cap of 2%, even if the index suggests a 3% increase, your rate will only rise by 2%. This safety net aids in managing unexpected spikes in monthly payments.
- Floor Security: Floors play a pivotal role, too. If the market rate falls, a floor ensures your interest rate won’t dip below a specified level. This means you can still face a higher payment compared to prevailing lower rates.
- Monitoring Index Changes: The index, which is a benchmark for the life of your ARM, directly affects your payment amount. For instance, if the index climbs to 3.5%, and your margin is 2%, your new interest rate becomes 5.5%, leading to increased payments.
- Financial Buffering: As rates shift, creating a financial cushion can shield you from potential financial strains. Aim to save at least 3-6 months’ worth of increased payments to alleviate stress during adjustment periods.
| Rate Changes | Initial Rate | After 1st Adjustment (2% Cap) | After 1st Adjustment (0% Cap) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Index at 2% | 3% | 5% | 5% |
| Index at 3% | 3% | 5% | 6% |
| Index at 4% | 3% | 5% | 7% |
Real-World Examples
Consider Jane, who has an ARM with a 2% cap. After her initial fixed-rate period, the market’s index rises to 4%. Instead of her rate increasing to 6%, it only adjusts to 5%. This cap saved her from a staggering $150 increase in her monthly payment, showcasing the protective aspect of caps in ARM agreements.
On the flip side, Mike has a different ARM with no cap on adjustments. When the index rises sharply to 5%, his payments leap from $1,200 to $1,500 immediately after the first adjustment. This stark increase emphasizes the risk associated with uncapped ARMs and highlights the importance of understanding the specific terms of your mortgage.
Practical Implications
- Regularly check the market index related to your ARM to anticipate changes in your payments.
- Make it a habit to review your mortgage terms—especially caps, floors, and margin—so you’re well aware of potential payment changes.
- Building a financial buffer to cover at least 3-6 months of potential increased payments is a proactive step you can take to ensure stable finances when rates rise.
- Use financial tools or calculators to simulate potential payment changes based on varying index rates to stay informed and prepared.
By actively monitoring these elements, you’re in a better position to respond to market changes and manage your ARM payments effectively.