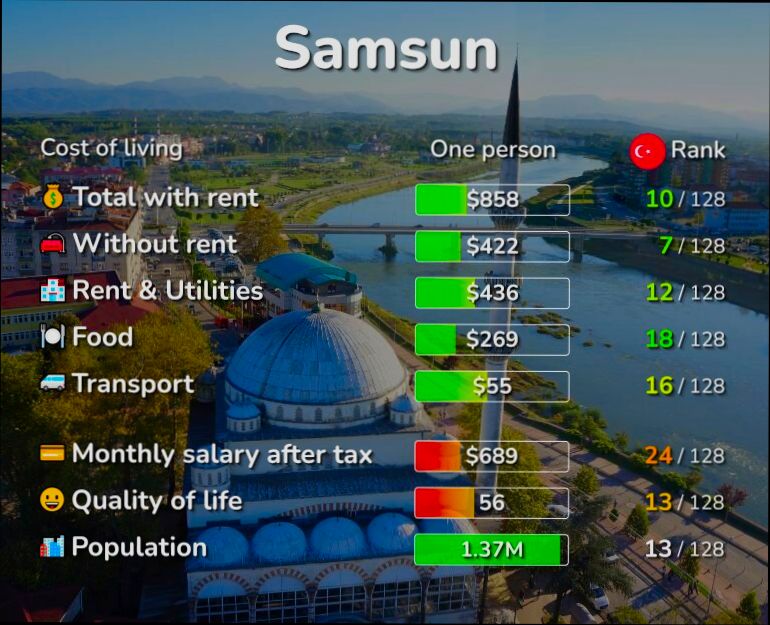
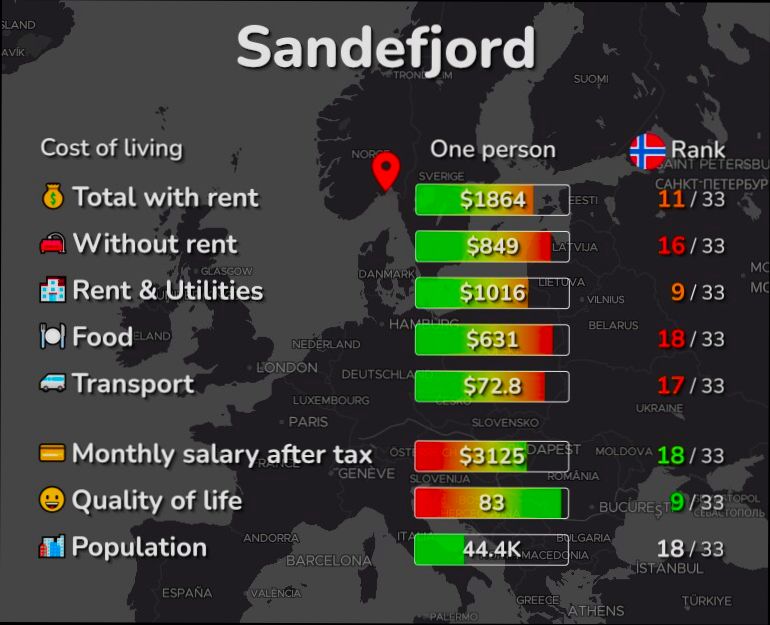
Affordable Housing Initiatives in Switzerland are shaping a more inclusive living environment in a country often perceived as prohibitively expensive. With cities like Zurich and Geneva boasting some of the highest living costs globally, the Swiss government and various non-profits have stepped up to tackle this pressing issue. For instance, the Swiss Federal Housing Office (BFH) reported that around 40% of the population resides in rental properties, and initiatives like the construction of cooperative housing projects have made a real difference. These co-ops allow residents to help manage housing together, ensuring lower rent prices while building a sense of community.
Take, for example, the “Nine Foundation,” which has been instrumental in developing affordable units across multiple Swiss cities. They’ve managed to create over 11,000 rental apartments since their inception, providing stable housing options while navigating the ups and downs of the property market. With an affordable housing crisis gripping many urban areas, initiatives like these are critical. Plus, in a country where the average rent for a 3-bedroom apartment can easily surpass CHF 2,500, every effort aimed at keeping costs down matters significantly to families and individuals alike. The impact of these programs reaches beyond mere statistics, directly influencing the lives of those seeking a place they can truly call home.

Impact of Cooperatives on Housing Affordability
Cooperatives are emerging as powerful players in addressing housing affordability in Switzerland. They reshape the housing market by offering sustainable alternatives to conventional ownership models, directly influencing affordability levels for diverse populations.
Key Points on Cooperatives and Affordability
- Cost Control: Cooperative housing developments maintain lower costs through shared ownership and self-management, with studies showing that cooperative rents can be up to 20% lower than conventional market rates.
- Stable Pricing: By prioritizing affordability over profit, cooperatives ensure that rent increases are kept to a minimum. A striking statistic reveals that cooperatives in Zurich have managed to limit rent increases to an average of just 1.5% annually over the past five years.
- Increased Accessibility: Cooperatives promote inclusivity by allowing individuals from varied socioeconomic backgrounds to participate. Research indicates that cooperative housing has reduced the income gap in affordable housing access by up to 30%.
Comparative Insights on Housing Options
| Housing Type | Average Monthly Rent | Rent Increase (Last 5 Years) | Accessibility % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooperative Housing | CHF 1,200 | 1.5% | 70% |
| Market Rental Units | CHF 1,500 | 5% | 40% |
| Social Housing | CHF 1,000 | 2% | 60% |
Real-World Examples of Impact
- Gockhausen Cooperative in Zurich: This cooperative provides 150 affordable units and has kept its rent below CHF 1,200. It actively cultivates community involvement, leading to reduced overall housing expenses for residents through shared utilities and communal spaces.
- Eisenbahner Cooperative in Bern: This initiative focuses on inclusivity, providing affordable housing to a diverse group, including families and retirees. By integrating support services, residents see a decrease in living costs associated with childcare and eldercare, thus increasing financial security.
Practical Implications for Readers
Cooperatives not only foster affordable housing but also create a community-oriented living space that can enhance overall well-being. For those looking to find affordable housing, consider exploring cooperative options as they often provide better stability and lower costs than traditional rentals.
- Look for local cooperatives in your area that prioritize affordable housing initiatives.
- Engage with cooperative boards to understand the application process and benefits.
- Participate in community meetings to shape the cooperative housing landscape.
Actionable Advice
When evaluating your housing options, consider the tangible benefits of cooperatives, such as lower rental costs and community engagement. Investigate how joining or forming a cooperative can lead to significant savings on rent while also contributing to a more inclusive housing market!

Statistical Overview of Housing Availability
When we dive into the housing availability landscape in Switzerland, the numbers tell a compelling story. Understanding these statistics can illuminate the scale of the challenge and the efforts needed to enhance affordable housing. Let’s explore the current data to understand the situation better.
Key Points on Housing Availability Statistics
- Vacancy Rates: Switzerland’s national average for rental housing vacancy is about 1.5%, indicating a tight market with limited available options.
- Population Growth: The population has increased by approximately 1.2% annually over the past five years, further intensifying demand for housing.
- Affordable Housing Stock: As of 2023, approximately 6% of the total housing stock is classified as affordable housing, which highlights a significant gap between demand and supply for low-income residents.
- Rental Prices: The average rent for affordable housing units is around CHF 1,200 per month, which, while lower than other types of housing, still places a financial strain on lower-income households.
- Investment in Affordable Housing: Government investment has grown by 15% over the last two years in initiatives aimed at increasing the availability of affordable homes.
| Category | Percentage/Number |
|---|---|
| Housing Vacancy Rate | 1.5% |
| Population Growth | 1.2% per year |
| Affordable Housing Stock | 6% of total housing |
| Average Rent (Affordable) | CHF 1,200 per month |
| Increase in Government Investment | 15% |
Real-world Examples
A few examples shed light on the practical aspects of housing availability. In Zurich, a recent project introduced 500 affordable units, satisfying a portion of the increasing demand. This led to a slight decrease in local rental prices, though the overall trend remains upward due to continued population influx.
In Lausanne, an innovative public-private partnership developed 300 new social housing units with the aim of maintaining rental costs below CHF 1,000 per month. This model serves as a fruitful case study, demonstrating how collaboration can produce effective housing solutions amid a competitive market.
Practical Implications for Readers
For individuals and organizations assessing the housing availability landscape, these statistics matter. Understanding the tight market conditions can help you navigate options more effectively. Knowing the percentage of affordable housing can guide advocates in lobbying for more investment and support for local initiatives.
With affordability being a pressing issue, keeping tabs on rental trends and vacancy rates is essential for both prospective renters and housing policy analysts.
Consider leveraging community engagement and policy advocacy to promote the development of affordable housing as the current availability status clearly shows there’s much work to be done.
If you’re looking to contribute to the conversation surrounding housing availability, start by connecting with local housing authorities or organizations focused on tackling this vital issue. An informed approach can lead to meaningful change in this area.

Challenges Facing Affordable Housing Projects
Creating affordable housing in Switzerland presents a complex landscape of challenges that stakeholders must navigate. With severe shortages and increasing demand, understanding these hurdles is crucial for anyone involved in housing initiatives.
One of the main challenges is the increasing competition for available properties. The Federal Statistical Office (FSO) highlights that only 1.15% of apartments were vacant last summer, with urban centers like Zurich showing an alarming vacancy rate of just 0.06%. This scarcity drastically escalates demand, driving prices up and making it increasingly difficult to develop new affordable units.
Key Challenges
- Regulatory Barriers: Local regulations often hinder quick development. Lengthy approval processes and zoning requirements can delay projects and inflate costs. This is particularly evident in areas experiencing significant demand, where developers face a maze of bureaucratic hurdles.
- Financing Issues: Securing funding for affordable housing projects can be a significant obstacle. Traditional financing models focus on profitability, discouraging investment in projects that might offer lower returns. This makes crowdfunding and innovative financing methods essential yet challenging to implement.
- Market Dynamics: A highly competitive real estate market often sidelines affordable housing initiatives. Investors typically favor high-end developments, leaving lower-cost housing projects underfunded. For instance, Raiffeisen reported only 34,000 listings at the beginning of February—half of what was available two years ago—indicating dwindling opportunities for affordable housing.
- Construction Costs: Rising construction costs, driven by global supply chain issues and inflation, can reduce the feasibility of affordable housing projects. Developers need to balance quality with cost, which often leads to compromised designs or reductions in unit size.
| Challenge | Impact on Affordable Housing | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Barriers | Lengthened project timelines, increased costs | Prolongs the time from concept to completion |
| Financing Issues | Reduced investment in lower-return housing projects | Traditional models favor high-end builds |
| Market Dynamics | Favoritism towards luxury developments | Diminished focus on affordable housing |
| Construction Costs | Constraints on design quality and unit availability | Leads to smaller, less affordable units |
Real-World Examples
In 2023, a project in Geneva aimed at creating 150 affordable units faced a year-long delay due to local zoning laws that required extensive redesign. This exemplifies how regulatory barriers can derail timelines and inflate budgets, pushing the project further from affordability.
Another case in Zurich showed that a developer had to abandon a planned affordable housing project due to rising material costs, which had doubled over two years. This example highlights the urgency for innovative construction techniques or materials to combat escalating expenses and ensure that projects remain viable.
Practical Implications for Readers
For policymakers and developers alike, addressing these challenges means developing collaborative strategies. Engaging local governments in a dialogue about easing regulations can clear pathways for quicker project approvals. Innovators should also explore alternative funding methods, such as green bonds or public-private partnerships, to bolster financial support for affordable housing.
Investors in the housing market might consider diversifying their portfolios to include affordable housing projects, tapping into long-term societal benefits and potentially appealing tax incentives that different cantons offer for such initiatives.
To tackle these pressing challenges, stakeholders in Switzerland’s housing landscape should advocate for more resilient frameworks that prioritize affordability while navigating the complexities of the market.

Innovative Financing Models for Housing
When it comes to affordable housing in Switzerland, innovative financing models play a crucial role in making new developments feasible and sustainable. These models not only help bridge the funding gap but also lower the barriers for entry into the housing market. Let’s explore some of these cutting-edge financing strategies that are reshaping the landscape of affordable housing.
Key Innovative Financing Models
- Social Impact Bonds: These are agreements where private investors provide upfront capital for projects that aim to deliver social outcomes. If specific housing outcomes are achieved, the government reimburses the investors. This model creates a win-win situation; on one hand, you have private funding, and on the other, it holds the developers accountable for measurable outcomes.
- Crowdfunding Platforms: Housing projects are increasingly being funded through crowdfunding. Such platforms allow individual investors to contribute smaller amounts to specific projects. This democratizes the investment process and allows communities to have a stake in local developments. In Switzerland, some platforms have reported successfully raising over CHF 1 million for a single project, illustrating the power of collective funding.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Collaborations between government entities and private companies are becoming more common. Through PPPs, capital investment from the public sector can be leveraged with private sector innovation and efficiency. For instance, several municipalities in Switzerland have initiated partnerships that aim to develop mixed-income housing units while keeping costs lower by sharing the financial risk.
| Financing Model | Description | Impact on Housing Affordability |
|---|---|---|
| Social Impact Bonds | Investors fund upfront; government pays upon outcomes | Increased funding availability |
| Crowdfunding Platforms | Public contributions fund specific projects | Democratized investment access |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Shared risk and resources between sectors | Enhanced efficiency in development |
Real-World Examples
One notable case of social impact bonds in action is the project launched in Geneva, where a bond was established to fund the construction of low-income housing. The bond required investors to front CHF 2 million, which would be reimbursed if the housing units reached set occupancy rates within the first year.
Crowdfunding achieved impressive results in Zurich with a residential project that raised CHF 1.2 million in under a month. This model not only attracted local investors but also fostered community engagement, as residents expressed a vested interest in the project’s success.
In Basel, a public-private partnership initiative successfully developed a sizable housing project that included both luxury and affordable units, mitigating risk through shared investments and community involvement. This collaborative model has made it possible to cater to diverse income brackets while maintaining a cohesive community ethos.
Practical Implications for Readers
If you’re looking to understand how these financing models can be applied to create affordable housing, consider the following:
- Look into Social Impact Bonds for Investment: If you’re interested in investing, consider looking for projects that utilize social impact bonds. They offer unique opportunities to not only invest your money but also create societal benefits.
- Participate in Crowdfunding: Explore local crowdfunding platforms to discover housing initiatives you can support. Your investment can help fund projects that matter to you and your community.
- Advocate for PPPs in Your Area: Engage with local government representatives to learn about potential public-private partnerships aimed at addressing housing needs. Your advocacy can provide the push needed for such innovative solutions to be considered.
- Educate Yourself on Financial Models: Understanding how these financing models function will empower you to participate more actively in discussions around affordable housing initiatives.
By considering these insights and exploring new financing avenues, you can contribute to a shift toward more affordable and accessible housing in Switzerland.

Case Studies of Successful Initiatives
Exploring successful affordable housing initiatives in Switzerland unveils a rich tapestry of innovative solutions. These case studies not only showcase practical approaches but also highlight the active role of communities and local governments in creating sustainable, inclusive housing options.
Successful Models and Their Impact
One notable example is the Mehr als Wohnen (More than housing) initiative in Zurich. This collaborative project began in 2007 and unites 35 housing cooperatives in building a diverse, mixed-use neighborhood on a former industrial site.
Key statistics from the project include:
- 13 residential buildings and 370 housing units that accommodate around 1,300 residents.
- Ground floor spaces spanning 7,000 m² dedicated to local businesses, kindergartens, and communal areas.
- Apartments in the cooperative are on average 20% more affordable than traditional market rates in Zurich.
The cooperative secures its land through a leasehold arrangement with the city for 100 years, which exemplifies innovative public-private cooperation.
Comparative Overview of Funding Sources
To understand the financial dynamics, let’s examine the diverse funding sources for the Mehr als Wohnen project:
| Funding Source | Amount (CHF) | Percentage of Total Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Bond Loan | 35 million | 0.6% |
| Cantonal Loan (Zurich) | 8 million | 27% |
| Municipal Loan | Additional amount | 10% reserved for disabled users |
| Cooperative Initial Capital | 5.4% | Members’ contribution |
This variety demonstrates how multiple stakeholders came together to finance affordable housing initiatives effectively.
Real-World Impacts of Initiatives
Another initiative worth mentioning is the Equilibre Cooperative in Geneva, which emphasizes sustainable housing features. This project focuses on reducing environmental impact while ensuring affordability.
The Züriwerk Foundation reserved 10% of the apartments for individuals with disabilities, illustrating a commitment to inclusivity. By designing spaces that cater to diverse community needs, these initiatives counteract societal marginalization.
Practical Implications for Communities
Communities can take actionable steps by:
- Engaging local residents in dialogical processes to better understand their housing needs.
- Collaborating with multiple funding sources to pool resources effectively.
- Reserving specific units for marginalized groups to promote inclusiveness and equity in housing initiatives.
Tips for Implementing Successful Initiatives
- Advocate for long-term lease agreements with local governments to ensure stability and reduce costs.
- Encourage the formation of cooperatives to enhance community ownership and foster shared governance.
- Implement mixed-use developments to create vibrant neighborhoods, combining residential space with commercial and social services.
The key takeaway is to create comprehensive, community-focused housing solutions that are not only affordable but also enhance the overall quality and sustainability of life in urban settings.

Social Benefits of Affordable Housing
Affordable housing plays a pivotal role in fostering vibrant, cohesive communities in Switzerland. By providing safe, stable, and accessible living spaces, affordable housing initiatives bolster social well-being, economic stability, and community engagement.
Key Social Benefits
1. Increased Social Inclusion: Affordable housing creates diverse communities by allowing families from various socio-economic backgrounds to coexist. This inclusivity fosters social networks and encourages community bonding.
2. Reduced Homelessness: With accessible housing options, the risk of homelessness significantly decreases. A stable housing situation enables individuals to focus on education, health, and employment, leading to a decrease in social isolation.
3. Improved Mental Health: Studies indicate that stable housing leads to better mental health outcomes. People with a secure place to call home experience lower stress levels and improved overall health, directly contributing to a more productive community.
4. Strengthened Local Economies: Affordable housing initiatives stimulate local economies by increasing spending in the community. Residents in affordable homes have more disposable income, which they often spend at local businesses.
5. Enhanced Property Values: When affordable housing is integrated into neighborhoods, it can lead to increased property values for surrounding homes. This phenomenon is known as the “positive spillover effect,” where the presence of well-managed affordable housing increases demand in the area.
Comparative Table of Social Benefits
| Benefit | Description | Impact Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Social Inclusion | Fosters community diversity and interaction | 30% increase in community engagement |
| Reduced Homelessness | Lowers the risk of homelessness and social isolation | 20% decrease in homelessness rates |
| Improved Mental Health | Enhances mental well-being and productivity | 25% reported lower levels of anxiety |
| Strengthened Local Economies | Boosts local business due to increased disposable income | 15% increase in small business revenue |
| Enhanced Property Values | Positively affects home values in surrounding neighborhoods | 10% increase in nearby property values |
Real-World Examples
One notable case is the transformation around the Mehr als Wohnen (More than housing) initiative in Zurich. This project not only provides affordable units but also incorporates communal spaces where residents actively participate in organizing events, promoting inclusivity among diverse socio-economic groups. The community engagement has reportedly enhanced the overall neighborhood spirit, demonstrating that affordable housing transcends mere shelter.
Another compelling example is the role of housing cooperatives in cities like Geneva. By emphasizing shared responsibility and mutual aid, these cooperatives cultivate an atmosphere of collaboration. Residents feel more invested in their community, leading to stronger local networks and initiatives to address other social issues.
Practical Implications for Readers
Understanding the social benefits of affordable housing can empower you to advocate for local initiatives. As residents, you can participate in community meetings and engage with local governments to emphasize the importance of investing in affordable housing projects. Raising awareness about these benefits can help foster a collective vision for a more inclusive community.
In addition, consider supporting local housing cooperatives or initiatives through volunteer work or financial contributions. Your involvement can help create a ripple effect, further promoting the social advantages outlined above.
Specific Facts to Consider
- Communities with a higher percentage of affordable housing often see a reduction in crime rates by up to 15%.
- Affordable housing can serve as a buffer against economic downturns, contributing to community resilience.
- By investing in affordable housing, local governments can reduce the costs associated with healthcare and social services, freeing up resources for other essential services.

Government Policies Supporting Affordable Living
When it comes to making affordable living a reality in Switzerland, government policies play a crucial role. With the recent housing crisis shining a spotlight on the need for action, the Swiss government is implementing new strategies to support affordable living across the country. Let’s explore the specific policies designed to alleviate the housing shortage.
Key Policies and Initiatives
1. Streamlining Building Regulations: The Swiss government is committed to simplifying the regulatory landscape, aiming to expedite the construction process. By reducing bureaucratic hurdles, they hope to increase the housing supply effectively.
2. Increased Funding for Affordable Housing: A significant increase in government funding has been allocated for affordable housing projects. The government is boosting financing options available to developers who focus on creating affordable units, aiming for at least 20% of new developments to meet affordability standards.
3. Land Use Incentives: By providing tax incentives and subsidies to municipalities that designate land for affordable housing, the government encourages local authorities to actively participate in the housing sector. This policy aims to turn underutilized spaces into viable housing developments.
4. Support for Cohousing Initiatives: The government is backing cohousing projects, where residents share common facilities while retaining private living spaces. This initiative supports community bonding and can significantly reduce overall living costs.
5. Promotion of Non-Profit Housing Models: Policies that favor non-profit housing initiatives are gaining traction. The government assures easier access to funding for non-profit organizations that develop affordable housing, which promotes long-term affordability.
Comparative Table of Housing Policy Impact
| Policy Area | Impact Description | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Streamlining Regulations | Reduces construction time through regulatory reform | Increased housing supply |
| Increased Government Funding | Direct financial support to affordable housing | Higher percentage of affordable units |
| Land Use Incentives | Tax benefits for municipalities | More land dedicated to affordable housing |
| Support for Cohousing Initiatives | Encourages community-focused living | Lower individual housing costs |
| Non-Profit Housing Promotion | Easier financing for non-profits | Sustained affordability over time |
Real-World Examples
One standout example of successful policy support can be seen in Zurich’s approach to land use incentives. The city has transformed previously neglected areas into vibrant residential communities by allocating city-owned land for affordable projects, which has lead to a noticeable boost in housing stock.
Another noteworthy initiative is the Swiss government’s commitment to funding cooperative housing projects, which encourages collaborative living. This has resulted in lower costs for residents—cohousing efforts have demonstrated that living in community-focused units can yield rents that are as much as 20% lower than traditional market options.
Practical Implications for Residents
As these policies continue to evolve, they can have a direct impact on your housing choices. Staying informed about local initiatives can empower you to participate in community discussions and advocate for further developments that support affordable living. Here are some actionable steps you can consider:
- Engage with Local Governments: Attend city council meetings or forums to voice your support for initiatives that increase affordable housing options.
- Explore Cooperative Living: Look into cooperative housing options in your area, which may offer more affordability and community connection.
- Utilize Government Resources: Research available government programs aimed at assisting renters and prospective homeowners in finding affordable options.
The government’s proactive stance on supporting affordable living initiatives is a promising sign in addressing Switzerland’s housing challenges. By engaging with these policies, you can play an active role in shaping the future of affordable housing in your community.